Research shows that age-related hearing decline happens as tiny hair cells in your inner ear gradually deteriorate, making it harder to understand speech, especially in noisy places. This natural process can cause frustration, social withdrawal, and even impact your emotional well-being. Using hearing aids, which have become more comfortable and effective, can markedly improve your quality of life. To learn how early action and technology can make a difference, keep exploring what the studies reveal.
Key Takeaways
- Research indicates that aging causes deterioration of inner ear hair cells, leading to gradual hearing loss.
- Studies show untreated age-related hearing decline is linked to social isolation and cognitive decline.
- Advances in hearing aid technology improve device comfort, discretion, and effectiveness, promoting early intervention.
- Early detection and use of hearing aids significantly enhance speech understanding and overall quality of life.
- Addressing hearing loss supports mental health, social engagement, and maintains communication abilities in older adults.

Have you ever noticed that your ability to hear clearly seems to decline as you get older? It’s a common experience that many people face, and research confirms that age-related hearing decline affects a significant portion of the population. As you age, the tiny hair cells in your inner ear, which are responsible for transmitting sound signals to your brain, gradually deteriorate. This process can lead to difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments. If you’re noticing these changes, hearing aids might be a helpful solution. These devices amplify sounds, making it easier to follow conversations and stay engaged with others. Many studies show that using hearing aids can dramatically improve quality of life by restoring a sense of connection and reducing frustration caused by missed words or misunderstood speech.
However, the decline in hearing isn’t just a matter of missing out on sounds. It often leads to social isolation, a serious concern backed by research. When you struggle to hear, you might feel embarrassed or frustrated, prompting you to withdraw from social interactions. Over time, this avoidance can become a habit, causing you to miss out on gatherings, conversations with family, or even casual chats with friends. Social isolation doesn’t just diminish your social life; it can also impact your mental health, increasing risks of depression and cognitive decline. Recognizing this link is vital because it highlights the importance of addressing hearing issues early. Using hearing aids not only helps improve auditory perception but also encourages you to stay socially active. Additionally, understanding the effects of age-related sensory decline can motivate early intervention.
The good news is that research shows early intervention makes a difference. When you get your hearing tested and start using hearing aids promptly, you’re more likely to maintain your social connections and mental sharpness. Advances in hearing aid technology mean these devices are more discreet, comfortable, and effective than ever before. They can be customized to fit your specific hearing needs, helping you regain confidence in your ability to communicate. Regular check-ups and adjustments guarantee your hearing aids continue to work at their best. Taking these steps not only improves your hearing but also helps prevent the cycle of social withdrawal that often accompanies untreated hearing loss. Ultimately, understanding the connection between age-related hearing decline and social isolation underscores the importance of proactive management—so you can stay connected, engaged, and vibrant as you age.
OTC Hearing Aids for Seniors, Nearly Invisible Rechargeable Hearing Aids, 100+ Hours of Charging Case Usage, Super-Mini Invisible Design, Comfort Fit in Ear Canal, AI Noise Cancellation and Clear Sound, Suitable for Various Daily Scenarios
【Hi-Fi Sound Quality】BIGPROT features an upgraded industry-leading smart chip with AI-powered dynamic noise cancellation, delivering true-to-life sound. With…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Hearing Loss Be Completely Prevented With Lifestyle Changes?
You might think lifestyle changes can fully prevent hearing loss, but that’s not entirely true. While lifestyle modifications and preventive measures, like avoiding loud noises and managing health issues, can reduce your risk, they can’t guarantee complete prevention. Age-related hearing decline is complex, and some factors are beyond control. Still, adopting healthy habits improves your chances of maintaining better hearing for longer.
Are Certain Professions More Susceptible to Age-Related Hearing Decline?
Certain professions are more susceptible to age-related hearing decline because of occupational noise exposure. If you work in loud environments, like construction or manufacturing, your risk increases. Prioritizing workplace safety measures, such as wearing hearing protection and limiting noise exposure, helps reduce this risk. Staying aware of occupational hazards and taking proactive steps can preserve your hearing health as you age, making a significant difference over time.
How Does Genetics Influence Age-Related Hearing Loss?
Ever wonder why some people lose their hearing faster? Genetic predisposition and hereditary factors play a big role. Your genes can influence how your ears age, making you more or less susceptible to hearing loss over time. These inherited traits might silently set the stage for decline, revealing how your DNA shapes your future. Understanding this connection can help you take steps to protect your hearing before it’s too late.
What Are the Latest Technological Advancements in Hearing Aids?
You’ll find that the latest hearing aids feature advanced wireless connectivity, allowing you to seamlessly pair with smartphones and other devices. AI integration enhances sound clarity and automatically adjusts to different environments, giving you a more natural listening experience. These innovations make hearing aids more intuitive and personalized, so you can stay connected and enjoy conversations without constantly adjusting settings. It’s all about making your hearing experience smarter and more convenient.
Is There a Link Between Age-Related Hearing Decline and Cognitive Health?
Imagine you notice your hearing gradually worsens, and soon, you start forgetting conversations. Research suggests a neurodegeneration connection, where age-related hearing decline correlates with cognitive decline. This link implies that untreated hearing loss may accelerate cognitive issues, increasing dementia risk. You should consider early hearing assessments and interventions, as addressing hearing health could help preserve your cognitive function and reduce the neurodegeneration connection over time.

Audien Atom One OTC Hearing Aids – Wireless, Rechargeable, and Comfortable | Clear Sound in a Small, Discreet Design for Seniors & Adults with Hearing Loss
Hear What Matters Most: Hearing isn’t one-size-fits-all. That’s why our adjustable frequency system lets you personalize your sound…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
As you read this, it’s no coincidence that many find their hearing gradually fading with age. Research shows this decline is common, but staying aware makes a difference. By taking proactive steps now, you might just prevent further loss or catch issues early. It’s almost as if the timing aligns perfectly—your actions today can shape how clearly you hear tomorrow. So, don’t wait; your future self will thank you for listening now.
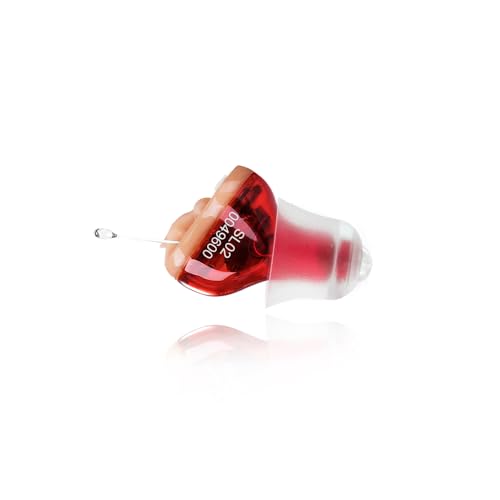

Hearing Aids for Seniors, Digital Hearing aid with Smart Noise Reduction chip,Clear Sound Quality and Comfortable Wearing
INVISIBLE & COMFORTABLE: This hearing aid is almost invisible, with highly advanced amplification technology, easy to hide and…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.

BOCOKO 2 Pieces Hearing Aid Clip Anti-Lost Lanyard BTE Protector for Adults Seniors and Kids(Black)
HEARING AID PROTECTION – Coming with a firm plastic clip, a silicone lanyard with two eye loops and…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.










